STATUS
Due to COVID-19 pandemic, LIGO-Virgo collaboration ended their O3b run on March 27, 2020 - just four days shy of original continuous O3 scheduled year; in October, 2019, a maintenance hiatus had resulted in a projected one-month operation extension.
Reported LIGO-Virgo trigger set, as of March 27, 2020, is comprised of N=71 non-rejected triggers (N=56 O3, N=11 O2, N=4 O1 [Nitz et al. 2020 N=4 additions
https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.3847/1538-4357/ab733f/pdf, with N=45 marginal events]), and N=24 O3 rejected triggers; events S190718y (>98% terrestrial/FAR 0.000000036484489800261.1514 per year) and S200105ae (97% terrestrial/FAR 24.21 per year) have not been retracted despite their technical non-cosmological identity, and are included in the non-rejected trigger count.
INTRODUCTION
Global and Continent-wide Blitzortung.org lightning ground flash data - as GIFs - for each of N=11+56 LIGO-Virgo high-confidence events and all N=24 retracted O3 events (as static images for Nitz et al. 2019 O2 N=4 additions due to Blitzortung server problems beginning October 2018, with new restrictions on non-member access of archive data) are presented herein; Nitz et al. 2020 N=4 additions and Zackay et al. 2019 "GW150916" https://arxiv.org/abs/1902.10331 are not included, as these are low-SNR data dredged events that are not universally-accepted as significant. It is expedient to download the otherwise inaccessible lightning GIFs from O1 and O2. The archive of 10 to 20-minute windows consisting of 100 frames in each case is ordered chronologically - from GW150914 on - immediately following plots of foreground persistent epochs with events. This series of plots is generally updated for all new triggers, and presents continuing measure-preserving interval restrictions with event parameter correlations.
Quasi-optimal foreground coupling conditions coinciding with all LIGO-Virgo triggers are left unexplained by LIGO-Virgo, despite that these putative gravitational wave arrivals uniquely co-occur with complex terrestrial foreground instability characterizing intermittent coherent geomagnetic conditions (sawtooth states), suitable for the generation of transverse transient artifacts, vorticity/vacuua/shocks, charge induction, and generalized critical/scale-invariant behavior in phase space.
Unusually active CG-dominated mesoscale thunderstorms occur in line-of-sight of L1-H1-V1 stations surrounding LIGO events, which is not unexpected considering geomagnetic storm/substorm/sawtooth event and global lightning event probability during these months suggested by ordered phase-preserving histograms and analytic functions of [wrapped] histograms for 5-min/day and day/yr resolution with binned LIGO triggers. Signal non-rejection is compounded by LIGO-Virgo active calibration - masking unstable magnetic ground state - and network feedback during geomagnetically-unstable periods, April 1, 2019 being no exception (space weather and lightning conditions being very similar to Jan. 4, 2017 conditions in relation to their magnetospheric cycles).
LIGO-Virgo Event-updated empirical histograms for foreground instability-annual stationary solar variability
data sources for introductory plots:
LIGO-Virgo O3 events
daily Sunspot number, 1818-present
SuperMAG substorm data
Most recent reported non-retracted trigger S200316bj:


Phase spectral density (DSTN2), autospectral density |ASDN|, from cyclical histograms of arrival times of all non-rejected LIGO-Virgo events, showing very sharp spectral modes and bifurcation preservation, as most other well-ordered/partitioned LIGO and solar-terrestrial physical datasets:


O3 histograms and robust arrival time analysis, emphasizing recurring numerical constants as pervasive eigenvalues, for whole sample and persisting upon application of same analyses to unretracted and retracted subsets:












A Pair of retracted NSBH ( S191120aj) and MassGap (S191120at) events that occurred bracketing strong periodic correlations 1/||(An-Bn)/(∑ (An,Bn))|| 5-min following event S191120aj and 5-min prior to event #S191120at, with interval ~225 minutes (as 6*37 minute prevailing [well-known recurring mode] magnetopause-ground lag):



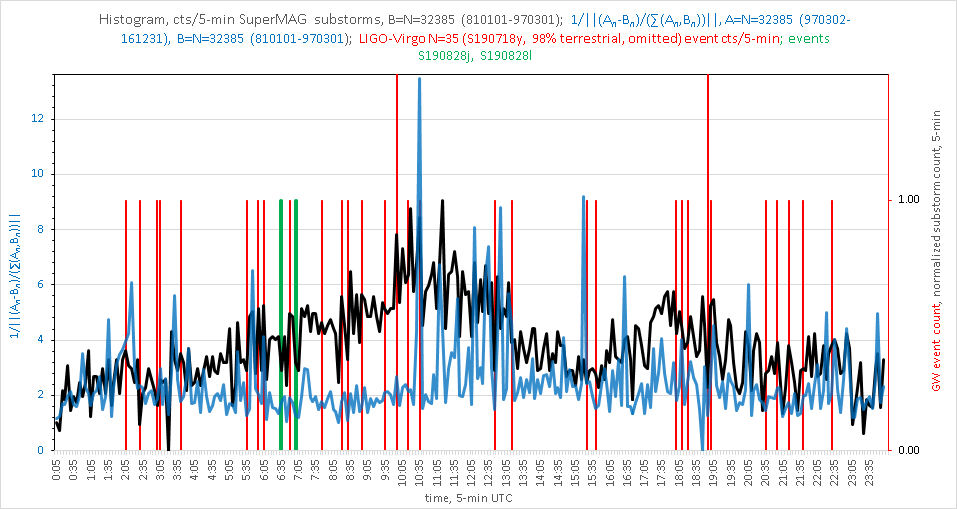
Histogram including retracted event S191117j with time collocation in cyclical daily continuous substorm region occupied by events S190727h and S190728q (as of event S190728q):

Very patently, LIGO events highlight little-known emergent effects of ionospheric-magnetospheric coupling during solar wind/interplanetary magnetic field driving. Lightning trigger driving is controlled by transverse global charge potential coherence, which shows shock profile, peak splitting, valley degeneracies, and numerical vorticity (fractional behavior). Atmospheric charge inversion/ionospheric emptying occurs during sawtooth injection events, which behave like structured superpositions of sub-scaled quasiperiodic sweeping/transverse/stepped reconnection-injection disturbances - promoting the conservation of an extended diffusion region with prolonged|lengthened transitional correlations in reconnection domain
Parametric properties of these systems are dual, self-affine, and inherently intermittent: stretching/contracting time symmetry and dipolarization oscillations/vacuua associated with rarefaction|contraction of multiple velocity converging-trailing CME shocks with singular shock profile, near-terrestrial/terrestrial particle acceleration. Open, coherent magnetic field bifurcation interacting with nonstationary, discretely lagged "frozen" interplanetary magnetic field partition [eigenmode-stream] correlations crossing over at saddle point instabilities/vacuua generate secondary magnetospheric delta shock waves. Sawtooth injections occur only ~11 times annually (mean calculated from last complete solar cycle - cycle 23 in its entirety is the only period yet available), which is identical to the total number of LIGO-Virgo events for O1-O2 year-equivalent network duty cycle given total quality data coverage. From September 14, 2015 to the end of August 2017 as LIGO operated (with an inoperative stage during most of 2016), evidence for sawtooth injection events with exceptional proton spikes, highly non-random magnetic field line density/coherence/orientation changes, and scattering-tunneling [false vacuum] behavior visible in unusual lightning activity - all coinciding during each GW detection. Prior peer-reviewed studies have identified properties of the magnetic components of Schumann resonances as problematic detector error sources that have prevented the study of a stochastic GW background.
https://journals.aps.org/prd/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevD.97.102007
https://arxiv.org/abs/1802.00885
HIGH-RESOLUTION CG LIGHTNING SURROUNDING LIGO-VIRGO EVENT WINDOWS
O1:
GW150914 event:
UTC 09:50:45, coincident with global, superimposed CG lightning at almost exact 10-minute intervals beginning with a sudden loss of CG activity sensed by the Blitzortung.org array in North America: ~9:40, ~(9:50, 10:00, 10:10, 10:20,...) and globally, with activity falling to zero at 9:40 and remaining at zero prior to a global superimposed/asymptotically-overlapping CG discharge burst at ~9:45 with stochastic continuity suddenly ceasing at 9:50, inverse of 10 minute North American region falling rate, with continental burst at 9:50 corresponding to final global burst oscillation episode.Unusually high global CG lightning activity detection is conceivably attenuated through sensor saturation, anomalous feedback, power loss, or instrumental clock error, with total CG remaining a significant artifact of pulse-coupled magnetospheric vacuum instability.




Bow shock-magnetopause and near-Earth activity during GW150914 (BATSRUS) https://iswa.ccmc.gsfc.nasa.gov/IswaSystemWebApp/index.jsp?:


GW151012 event: UTC 09∶54:43



http://www.srl.caltech.edu/ACE/ASC/DATA/level3/mag/ACESpec.cgi?LATEST=1
Bow shock-magnetopause and near-Earth activity during GW151012 (BATSRUS) https://iswa.ccmc.gsfc.nasa.gov/IswaSystemWebApp/index.jsp?:


GW151226 event: UTC 03:38:53


 http://www.srl.caltech.edu/ACE/ASC/DATA/level3/mag/ACESpec.cgi?LATEST=1
http://www.srl.caltech.edu/ACE/ASC/DATA/level3/mag/ACESpec.cgi?LATEST=1
Bow shock-magnetopause and near-Earth activity during GW151226 (BATSRUS) https://iswa.ccmc.gsfc.nasa.gov/IswaSystemWebApp/index.jsp?:


O2:
GW170104 event: UTC 10∶11:58


 http://www.srl.caltech.edu/ACE/ASC/DATA/level3/mag/ACESpec.cgi?LATEST=1
http://www.srl.caltech.edu/ACE/ASC/DATA/level3/mag/ACESpec.cgi?LATEST=1
Bow shock-magnetopause and near-Earth activity during GW170104 (BATSRUS) https://iswa.ccmc.gsfc.nasa.gov/IswaSystemWebApp/index.jsp?:


GW170729 event: UTC 18:56:29






























































event S190408an, 2019-0408, 18:18:02 UTC:




event S190923y, 2019-0923 12:56:22 UTC:


event S190924h, 2019-0924 02:19:15 UTC:


event S190928c, 2019-0928 02:14:18 UTC [retracted]:


A month-long LIGO observation hiatus was quietly announced July 12, 2019 https://twitter.com/Fulguritics/status/1179831916041654273, after the last two LVC events arrived highly correlated to solar flare prompt geomagnetic disturbance; ramifications of this interruption were not made public until October 1, 2019, on the day that this operational hiatus was scheduled to begin. Following the original July announcement, the next LVC event was problematic S190718y, a putative BNS trigger that remains unretracted at 98% terrestrial probability. S190718y may have similar signal and noise properties to GW170817 (itself only salvaged given excessive disordered noise/"glitches" due to desired association with GRB170817/AT2017gfo), and its outright rejection would cast doubt on decision to promote GW170817 as GW signal of BNS merger.
See modules on this blog for GW170817/GRB170817A/AT2017gfo/NGC4993:
https://fulguritics.blogspot.com/2018/06/gw170817-occurs-at-green-bar.html
https://fulguritics.blogspot.com/2018/10/why-is-information-on-ngc-4993.html
https://fulguritics.blogspot.com/2018/10/a-short-grb-analogue-with-multi.html
Paired events S190930s and S190930t (S190930t a single detector trigger - absolutely unreliable https://twitter.com/Fulguritics/status/1179844395677274112), their interval identical to solar wind arrival from instability between L1 and asymmetrical bow shock terminate a 33-day non-random/cyclically-correlated arrival block of LIGO-Virgo triggers, GPS clock error patent, similar to S190718y, 98% terrestrial BNS trigger and still unretracted.
https://twitter.com/Fulguritics/status/1179907360254390272
https://twitter.com/Fulguritics/status/1180028237658783744:





event S190930s, 2019-0930 13:36:02 UTC:


event S190930t, 2019-0930 14:34:27 UTC:


event S191105e, 2019-1105 14:35:45 UTC,















event S200114f 1263002916.24Jan. 14, 2020 02:08:18 UTC:
#S200114f #LIGO-Virgo trigger; no class, source prob, or DL, but narrow sky loc.
O2 GW170608/GW170818 ToA in same 25-min. window, like other proximal triggers.
#S200114f 02:08:18 UTC, Burst transient, CWB search, at central freq. 64.69 [Hz] lasting 0.01 sec. gcn.gsfc.nasa.gov/notices_l/S200
burst transient, 02:08:46 UTC; coherent shock sequence at L1 00:52-1:38 UTC, invariant solar wind v:lag ensemble converge at LVC event, w/central freq., 64.69 Hz as central val. for 10th Schumann res. mode ~64.62 Hz|0.88 c arxiv.org/pdf/1707.09047
10th Schumann resonance mode
model 1: 65.52 Hz
model 2: 63.72 Hz
mean 64.62 hz
(quasiperiodic correlation|sawtooth/shear/injection/ saddle modes)
burst is already propaganda. Many LVC events have false alarm rates of >1/year: "As Andy said...gravitational wave detectors do sometimes detect false positives, about once every 25 years. So that is something to keep in mind." earthsky.org/space/ligo-gra














RETRACTED #LIGO-Virgo #S200303ba 12:15:48 UTC BBH 86% FAR 1/2.4086 yrs NO CLOCK ERROR! burst-synced global CG #lightning photos.app.goo.gl/pv7UVxPVtrvBys #spaceweather [cf. unretracted #S200302c BBH 89% FAR 1/3.3894 yrs, clock error, mirror point correlation w/S200303ba, sawtooth event]

event S200308e, 2020-0308 01:19:27 UTC retracted:






event S200311bg, 2020-0311 11:58:53 UTC:













https://twitter.com/Fulguritics/status/1259250554187833344
#LIGO-Virgo #O3isHere putative #GravitationalWaves population over-correlated; squared, golden, cubic modes intrinsic w/magnetosphere-ground coupling; resonant gaps preserved between O3 retractions and non-retractions (e.g. retractions[60, 129]≈non-retractions[62, 130]≈0.43|𝐾
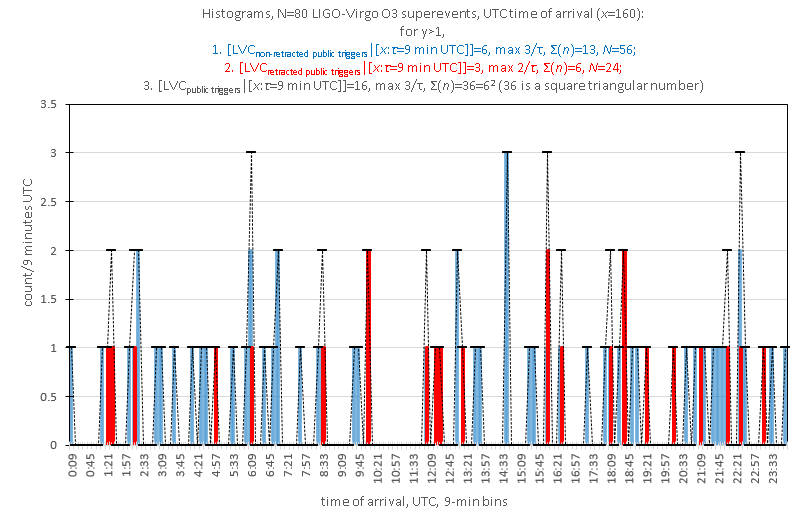
#LIGO-Virgo #O3isHere putative #GravitationalWaves population over-correlated; squared, golden, cubic modes intrinsic w/magnetosphere-ground coupling; resonant gaps preserved between O3 retractions and non-retractions (e.g. retractions[60, 129]≈non-retractions[62, 130]≈0.43|𝐾

Virgo events, in this case with retractions and non-retractions combined as a population. Strong integer-irrational scaling precludes LIGO claims of uncorrelated events.
Fourier modes: non-retracted[(130-62)/𝐾]≈retracted[(129-60)/𝐾]≈0.43, 𝐾=160
for 𝑁=56 non-retractions and 𝑁=24 retractions:

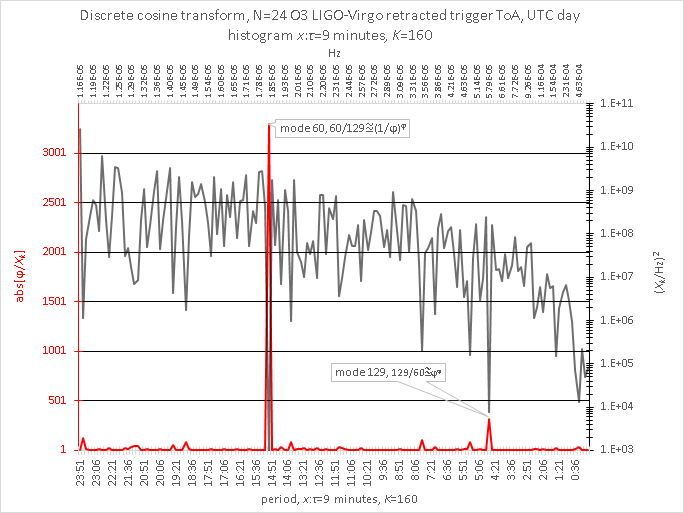
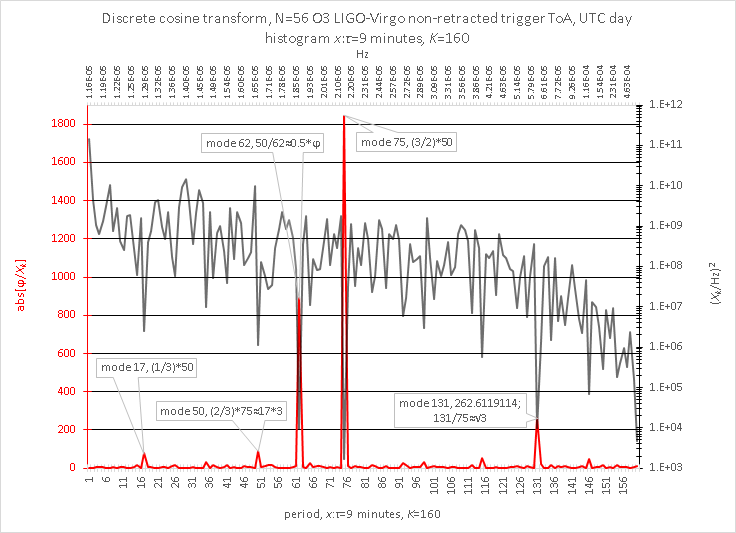
𝑁=56 non-retracted, 𝑁=24 retracted 1/(56/24)≈0.43
see Extreme conservation of constants for multiple [bound] degrees of freedom: neutrons, neutrinos, LVC events, Schumann resonances, ...
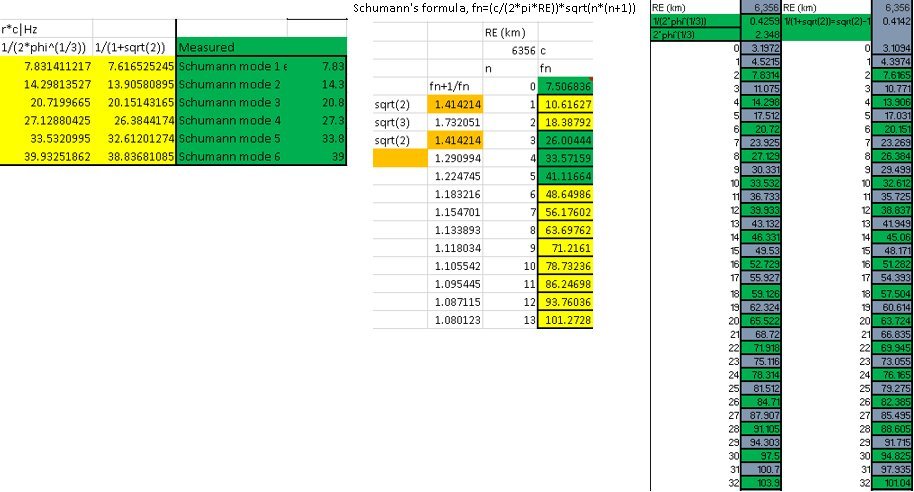
Precision non-empirical Schumann peaks:
v|c:≈0.43, r=1/(2φ^(1/3))=0.42589... f0=(rc/(2πRE)) fn=(rc/(2πRE))√(n(n+1)), for n2,n4,...
A. Cai-Clauer 2013 solar cycle 23 sawtooth event list (annual) max N=19, mid[mean, max]=15, mean N=11
https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/2013JA018819 B. O1-O2 events: Nitz et al 2018 N=11, Nitz et al 2020 N=15
https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.3847/1538-4357/ab733f/meta C. O3: N=56 confident, N=24 retracted LIGO-Virgo triggers 19*3:≃O3 confident events 24/15=1.6 (24/19)^2≈1.6
Nitz et al. 2020 additions do not break foreground correlations for events as class of ground coupling responsesFourier modes: non-retracted[(130-62)/𝐾]≈retracted[(129-60)/𝐾]≈0.43, 𝐾=160
for 𝑁=56 non-retractions and 𝑁=24 retractions:



𝑁=56 non-retracted, 𝑁=24 retracted 1/(56/24)≈0.43
see Extreme conservation of constants for multiple [bound] degrees of freedom: neutrons, neutrinos, LVC events, Schumann resonances, ...
Precision non-empirical Schumann peaks:
v|c:≈0.43, r=1/(2φ^(1/3))=0.42589... f0=(rc/(2πRE)) fn=(rc/(2πRE))√(n(n+1)), for n2,n4,...

A. Cai-Clauer 2013 solar cycle 23 sawtooth event list (annual) max N=19, mid[mean, max]=15, mean N=11
https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/2013JA018819 B. O1-O2 events: Nitz et al 2018 N=11, Nitz et al 2020 N=15
https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.3847/1538-4357/ab733f/meta C. O3: N=56 confident, N=24 retracted LIGO-Virgo triggers 19*3:≃O3 confident events 24/15=1.6 (24/19)^2≈1.6







A Pair of retracted NSBH ( S191120aj) and MassGap (S191120at) events that occurred bracketing strong periodic correlations 1/||(An-Bn)/(∑ (An,Bn))|| 5-min following event S191120aj and 5-min prior to event #S191120at, with interval ~225 minutes (as 6*37 minute prevailing [well-known recurring mode] magnetopause-ground lag):



Histogram including retracted event S191117j with time collocation in cyclical daily continuous substorm region occupied by events S190727h and S190728q (as of event S190728q):


Parametric properties of these systems are dual, self-affine, and inherently intermittent: stretching/contracting time symmetry and dipolarization oscillations/vacuua associated with rarefaction|contraction of multiple velocity converging-trailing CME shocks with singular shock profile, near-terrestrial/terrestrial particle acceleration. Open, coherent magnetic field bifurcation interacting with nonstationary, discretely lagged "frozen" interplanetary magnetic field partition [eigenmode-stream] correlations crossing over at saddle point instabilities/vacuua generate secondary magnetospheric delta shock waves. Sawtooth injections occur only ~11 times annually (mean calculated from last complete solar cycle - cycle 23 in its entirety is the only period yet available), which is identical to the total number of LIGO-Virgo events for O1-O2 year-equivalent network duty cycle given total quality data coverage. From September 14, 2015 to the end of August 2017 as LIGO operated (with an inoperative stage during most of 2016), evidence for sawtooth injection events with exceptional proton spikes, highly non-random magnetic field line density/coherence/orientation changes, and scattering-tunneling [false vacuum] behavior visible in unusual lightning activity - all coinciding during each GW detection. Prior peer-reviewed studies have identified properties of the magnetic components of Schumann resonances as problematic detector error sources that have prevented the study of a stochastic GW background.
https://journals.aps.org/prd/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevD.97.102007
https://arxiv.org/abs/1802.00885
HIGH-RESOLUTION CG LIGHTNING SURROUNDING LIGO-VIRGO EVENT WINDOWS
O1:
GW150914 event:
UTC 09:50:45, coincident with global, superimposed CG lightning at almost exact 10-minute intervals beginning with a sudden loss of CG activity sensed by the Blitzortung.org array in North America: ~9:40, ~(9:50, 10:00, 10:10, 10:20,...) and globally, with activity falling to zero at 9:40 and remaining at zero prior to a global superimposed/asymptotically-overlapping CG discharge burst at ~9:45 with stochastic continuity suddenly ceasing at 9:50, inverse of 10 minute North American region falling rate, with continental burst at 9:50 corresponding to final global burst oscillation episode.Unusually high global CG lightning activity detection is conceivably attenuated through sensor saturation, anomalous feedback, power loss, or instrumental clock error, with total CG remaining a significant artifact of pulse-coupled magnetospheric vacuum instability.





Bow shock-magnetopause and near-Earth activity during GW150914 (BATSRUS) https://iswa.ccmc.gsfc.nasa.gov/IswaSystemWebApp/index.jsp?:





http://www.srl.caltech.edu/ACE/ASC/DATA/level3/mag/ACESpec.cgi?LATEST=1
Bow shock-magnetopause and near-Earth activity during GW151012 (BATSRUS) https://iswa.ccmc.gsfc.nasa.gov/IswaSystemWebApp/index.jsp?:


GW151226 event: UTC 03:38:53


 http://www.srl.caltech.edu/ACE/ASC/DATA/level3/mag/ACESpec.cgi?LATEST=1
http://www.srl.caltech.edu/ACE/ASC/DATA/level3/mag/ACESpec.cgi?LATEST=1 Bow shock-magnetopause and near-Earth activity during GW151226 (BATSRUS) https://iswa.ccmc.gsfc.nasa.gov/IswaSystemWebApp/index.jsp?:


O2:
GW170104 event: UTC 10∶11:58


 http://www.srl.caltech.edu/ACE/ASC/DATA/level3/mag/ACESpec.cgi?LATEST=1
http://www.srl.caltech.edu/ACE/ASC/DATA/level3/mag/ACESpec.cgi?LATEST=1Bow shock-magnetopause and near-Earth activity during GW170104 (BATSRUS) https://iswa.ccmc.gsfc.nasa.gov/IswaSystemWebApp/index.jsp?:


http://www.srl.caltech.edu/ACE/ASC/DATA/level3/mag/ACESpec.cgi?LATEST=1
Bow shock-magnetopause and near-Earth activity during GW170608 (BATSRUS) https://iswa.ccmc.gsfc.nasa.gov/IswaSystemWebApp/index.jsp?:


Bow shock-magnetopause and near-Earth activity during GW170608 (BATSRUS) https://iswa.ccmc.gsfc.nasa.gov/IswaSystemWebApp/index.jsp?:


GW170729 event: UTC 18:56:29



http://www.srl.caltech.edu/ACE/ASC/DATA/level3/mag/ACESpec.cgi?LATEST=1
Bow shock-magnetopause and near-Earth activity during GW170729 (BATSRUS) https://iswa.ccmc.gsfc.nasa.gov/IswaSystemWebApp/index.jsp?:


GW170809 event: UTC 08:28:21



Bow shock-magnetopause and near-Earth activity during GW170729 (BATSRUS) https://iswa.ccmc.gsfc.nasa.gov/IswaSystemWebApp/index.jsp?:


GW170809 event: UTC 08:28:21



http://www.srl.caltech.edu/ACE/ASC/DATA/level3/mag/ACESpec.cgi?LATEST=1
Bow shock-magnetopause and near-Earth activity during GW170809 (BATSRUS) NO DATA (highly unsettled geostationary environment: interplanetary shocks, initial interplanetary storm peaking during GW1700817-GW170818, upon 8-day phase, and terminating 5 days subsequent during period of GW170823 trigger) https://iswa.ccmc.gsfc.nasa.gov/IswaSystemWebApp/index.jsp?:

GW170814 event: UTC 10∶30:43



Bow shock-magnetopause and near-Earth activity during GW170809 (BATSRUS) NO DATA (highly unsettled geostationary environment: interplanetary shocks, initial interplanetary storm peaking during GW1700817-GW170818, upon 8-day phase, and terminating 5 days subsequent during period of GW170823 trigger) https://iswa.ccmc.gsfc.nasa.gov/IswaSystemWebApp/index.jsp?:

GW170814 event: UTC 10∶30:43



http://www.srl.caltech.edu/ACE/ASC/DATA/level3/mag/ACESpec.cgi?LATEST=1
Bow shock-magnetopause and near-Earth activity during GW170814 (BATSRUS) https://iswa.ccmc.gsfc.nasa.gov/IswaSystemWebApp/index.jsp?:


Bow shock-magnetopause and near-Earth activity during GW170814 (BATSRUS) https://iswa.ccmc.gsfc.nasa.gov/IswaSystemWebApp/index.jsp?:


GW170817 event: UTC 12∶41:04


 http://www.srl.caltech.edu/ACE/ASC/DATA/level3/mag/ACESpec.cgi?LATEST=1
http://www.srl.caltech.edu/ACE/ASC/DATA/level3/mag/ACESpec.cgi?LATEST=1
Bow shock-magnetopause and near-Earth activity during GW170817 (BATSRUS) https://iswa.ccmc.gsfc.nasa.gov/IswaSystemWebApp/index.jsp?:


GW170818 event: UTC 02:25:09



 http://www.srl.caltech.edu/ACE/ASC/DATA/level3/mag/ACESpec.cgi?LATEST=1
http://www.srl.caltech.edu/ACE/ASC/DATA/level3/mag/ACESpec.cgi?LATEST=1Bow shock-magnetopause and near-Earth activity during GW170817 (BATSRUS) https://iswa.ccmc.gsfc.nasa.gov/IswaSystemWebApp/index.jsp?:


GW170818 event: UTC 02:25:09



http://www.srl.caltech.edu/ACE/ASC/DATA/level3/mag/ACESpec.cgi?LATEST=1
Bow shock-magnetopause and near-Earth activity during GW170818 (BATSRUS) https://iswa.ccmc.gsfc.nasa.gov/IswaSystemWebApp/index.jsp?:



GW170823 event: UTC 13:13:58



Bow shock-magnetopause and near-Earth activity during GW170818 (BATSRUS) https://iswa.ccmc.gsfc.nasa.gov/IswaSystemWebApp/index.jsp?:



GW170823 event: UTC 13:13:58



http://www.srl.caltech.edu/ACE/ASC/DATA/level3/mag/ACESpec.cgi?LATEST=1
Bow shock-magnetopause and near-Earth activity during GW170823 (BATSRUS) https://iswa.ccmc.gsfc.nasa.gov/IswaSystemWebApp/index.jsp?:


O3:
LIGO-Virgo science run O3 began April 1, 2019, which coincided with similar CG lightning conditions to prior ensembles during O1-O2 between GW triggers and further correlations in space weather and solar behavior, including the progressive closure of the trans-equatorial open granulation extending between two very stable solar polar coronal holes; these are compared to a growing array of ≤15 min samples of CG immediately surrounding claimed GW triggers. One should consider that CG lightning is not constant in time and space, and as such the very co-occurrence of GW signal times and unusual peak periods for CG discharge rate is statistically significant, with most sensed CG lightning relative to global activity occurring in intervals active in LOS of Livingston station during GW triggers, controlled by coupled vacuum shocks:
GW170104 and April 1, 2019 during first hours O3 with strikingly similar CG lightning orientations. This coincidence can bias noise analysis for estimation of false alarm rates:


O3 reported triggers, North America, around events (including all retracted triggers):
































Bow shock-magnetopause and near-Earth activity during GW170823 (BATSRUS) https://iswa.ccmc.gsfc.nasa.gov/IswaSystemWebApp/index.jsp?:


O3:
LIGO-Virgo science run O3 began April 1, 2019, which coincided with similar CG lightning conditions to prior ensembles during O1-O2 between GW triggers and further correlations in space weather and solar behavior, including the progressive closure of the trans-equatorial open granulation extending between two very stable solar polar coronal holes; these are compared to a growing array of ≤15 min samples of CG immediately surrounding claimed GW triggers. One should consider that CG lightning is not constant in time and space, and as such the very co-occurrence of GW signal times and unusual peak periods for CG discharge rate is statistically significant, with most sensed CG lightning relative to global activity occurring in intervals active in LOS of Livingston station during GW triggers, controlled by coupled vacuum shocks:
GW170104 and April 1, 2019 during first hours O3 with strikingly similar CG lightning orientations. This coincidence can bias noise analysis for estimation of false alarm rates:


O3 reported triggers, North America, around events (including all retracted triggers):
























































































event S190405ar, 2019-0405 16:01:56 UTC - quietly RETRACTED after GCN notice issued on April 12, as new event announced - obvious thunderstorm association with Livingston further bolsters well-documented sensitivity of LIGO network to lightning activity, which produced an instrumental transient waveform that was selected by matched filter designed to isolate GW candidates; another rejected trigger, of N=43 O1+O2 rejected triggers, was recorded on 2017-0405 during O2:


event S190408an, 2019-0408, 18:18:02 UTC:


event GW190412/S190412m, 2019-0412, 05:30:44 UTC (5:31:03); a rejected trigger, of N=43 O1+O2 rejected triggers, was recorded on 2017-0412 during O2:


event S190421ar, 2019-0421 21:39:16 UTC (event, upon EM follow up is 96% terrestrial, 4% BBH; UPDATE: May 3, 2019, event upgraded to 97% BBH, 3% terrestrial, following a two-week release/retraction/quota cycle, where new events correspond to the days of revisions, possibly corresponding to upgraded priors/bias as Bayesian confidence incestuously feeds on itself):


event GW190425/S190425z, 2019-0425 08:18:26 UTC:


event S190426c, 2019-0426 15:22:15 UTC:

event S190503bf 2019-0503 18:54:26 UTC:


event S190510g 2019-0510, 03:00:03 UTC - possible retraction. See
https://twitter.com/Fulguritics/status/1127382977237987328,
https://twitter.com/Fulguritics/status/1127360857606905857
https://twitter.com/cosmos4u/status/1127310136580689921:

event S190512at, 2019-0512 18:07:42 UTC:


event S190513bm, 2019-0513, 20:54:48 UTC:


event S190517h, 2019-0517, 05:51:23 UTC:


retracted trigger S190518bb
https://twitter.com/Fulguritics/status/1129950066255515650
https://twitter.com/Fulguritics/status/1129891867469012993

event S190519bj 2019-0519, 15:36:04 UTC:


event S190521g ,2019-0521 03:02:49 UTC:


event S190521r, 2019-0521 07:44:22 UTC:


event S190524q, 2019-0524 04:52:30 UTC [retracted]:


event S190602aq, 2019-0602 17:59:51 UTC;


event S190630ag, 2019-0630 18:52:27 UTC:

event S190701ah, 2019-0701 20:33:45 UTC:


event S190706ai, 2019-0706 22:26:57 UTC:


event S190707q, 2019-0707 09:33:44 UTC:


event S190718y, 2019-0718 14:35:32 UTC - not yet retracted, but as of 2019-0723, event considered 98% terrestrial in origin:



event S190720a, 2019-0720 00:08:53 UTC:

event S190727h, 2019-0727 06:03:51 UTC:


event S190728q, 2019-0728 06:45:27 UTC:

event S190808ae, 2019-0808 22:21:43 UTC (promptly retracted):


event GW190814/S190814bv, 2019-0814 21:11:18 UTC:


event S190816i, 2019-0816 13:05:10 UTC (retracted):

event S190822c, 2019-0822 01:30:23 UTC (retracted):


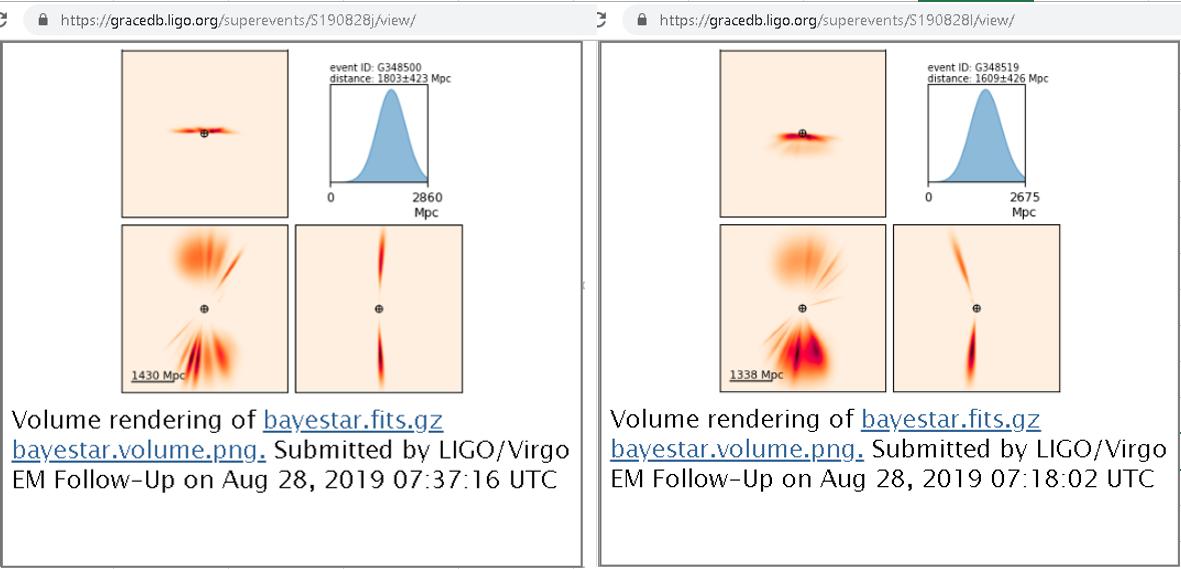
events S190828j, 2019-0828 06:34:21 UTC, and S190828l, 2019-0828 06:55:26 UTC, with 21 minute interval between events, identical to known late August sawtooth noise intervals reported in 2017 during O2. LIGO denies a multiple lensing hypothesis is applicable to these unusually similar events, which are considered to be BBH sources having almost identical luminosity distance estimation and prima facie source direction/sky localization probability range. Of course, no LIGO events are gravitational wave events, but LIGO-Virgo collaboration have already been enabled through a general breakdown of scientific impartiality to permit false positive error to run amok.
event S190828j, 2019-0828 06:34:21 UTC:


event S190828l, 2019-0828 06:55:26 UTC:





event S190829u, 2019-0829 21:06:17 UTC (retracted):


event S190901ap, 2019-0901 23:31:22 UTC:


event S190910d, 1252113997.242019-0910 01:26:19 UTC:


event S190910h, 1252139416.542019-0910, 08:29:58 UTC:


event S190915ak 2019-0915 23:57:23 UTC:


event S190421ar, 2019-0421 21:39:16 UTC (event, upon EM follow up is 96% terrestrial, 4% BBH; UPDATE: May 3, 2019, event upgraded to 97% BBH, 3% terrestrial, following a two-week release/retraction/quota cycle, where new events correspond to the days of revisions, possibly corresponding to upgraded priors/bias as Bayesian confidence incestuously feeds on itself):


event GW190425/S190425z, 2019-0425 08:18:26 UTC:


event S190426c, 2019-0426 15:22:15 UTC:


event S190503bf 2019-0503 18:54:26 UTC:


event S190510g 2019-0510, 03:00:03 UTC - possible retraction. See
https://twitter.com/Fulguritics/status/1127382977237987328,
https://twitter.com/Fulguritics/status/1127360857606905857
https://twitter.com/cosmos4u/status/1127310136580689921:


event S190512at, 2019-0512 18:07:42 UTC:


event S190513bm, 2019-0513, 20:54:48 UTC:


event S190517h, 2019-0517, 05:51:23 UTC:


retracted trigger S190518bb
https://twitter.com/Fulguritics/status/1129950066255515650
https://twitter.com/Fulguritics/status/1129891867469012993


event S190519bj 2019-0519, 15:36:04 UTC:


event S190521g ,2019-0521 03:02:49 UTC:


event S190521r, 2019-0521 07:44:22 UTC:


event S190524q, 2019-0524 04:52:30 UTC [retracted]:


event S190602aq, 2019-0602 17:59:51 UTC;


event S190630ag, 2019-0630 18:52:27 UTC:


event S190701ah, 2019-0701 20:33:45 UTC:


event S190706ai, 2019-0706 22:26:57 UTC:




event S190718y, 2019-0718 14:35:32 UTC - not yet retracted, but as of 2019-0723, event considered 98% terrestrial in origin:



event S190720a, 2019-0720 00:08:53 UTC:


event S190727h, 2019-0727 06:03:51 UTC:


event S190728q, 2019-0728 06:45:27 UTC:


event S190808ae, 2019-0808 22:21:43 UTC (promptly retracted):


event GW190814/S190814bv, 2019-0814 21:11:18 UTC:


event S190816i, 2019-0816 13:05:10 UTC (retracted):


event S190822c, 2019-0822 01:30:23 UTC (retracted):


events S190828j, 2019-0828 06:34:21 UTC, and S190828l, 2019-0828 06:55:26 UTC, with 21 minute interval between events, identical to known late August sawtooth noise intervals reported in 2017 during O2. LIGO denies a multiple lensing hypothesis is applicable to these unusually similar events, which are considered to be BBH sources having almost identical luminosity distance estimation and prima facie source direction/sky localization probability range. Of course, no LIGO events are gravitational wave events, but LIGO-Virgo collaboration have already been enabled through a general breakdown of scientific impartiality to permit false positive error to run amok.
global CG for both events: 



event S190828l, 2019-0828 06:55:26 UTC:


https://alog.ligo-wa.caltech.edu/aLOG/index.php?callRep=38410
https://alog.ligo-wa.caltech.edu/aLOG/index.php?callRep=38407




event S190829u, 2019-0829 21:06:17 UTC (retracted):


event S190901ap, 2019-0901 23:31:22 UTC:


event S190910d, 1252113997.242019-0910 01:26:19 UTC:


event S190910h, 1252139416.542019-0910, 08:29:58 UTC:




event S190923y, 2019-0923 12:56:22 UTC:


event S190924h, 2019-0924 02:19:15 UTC:


event S190928c, 2019-0928 02:14:18 UTC [retracted]:


A month-long LIGO observation hiatus was quietly announced July 12, 2019 https://twitter.com/Fulguritics/status/1179831916041654273, after the last two LVC events arrived highly correlated to solar flare prompt geomagnetic disturbance; ramifications of this interruption were not made public until October 1, 2019, on the day that this operational hiatus was scheduled to begin. Following the original July announcement, the next LVC event was problematic S190718y, a putative BNS trigger that remains unretracted at 98% terrestrial probability. S190718y may have similar signal and noise properties to GW170817 (itself only salvaged given excessive disordered noise/"glitches" due to desired association with GRB170817/AT2017gfo), and its outright rejection would cast doubt on decision to promote GW170817 as GW signal of BNS merger.
See modules on this blog for GW170817/GRB170817A/AT2017gfo/NGC4993:
https://fulguritics.blogspot.com/2018/06/gw170817-occurs-at-green-bar.html
https://fulguritics.blogspot.com/2018/10/why-is-information-on-ngc-4993.html
https://fulguritics.blogspot.com/2018/10/a-short-grb-analogue-with-multi.html
Paired events S190930s and S190930t (S190930t a single detector trigger - absolutely unreliable https://twitter.com/Fulguritics/status/1179844395677274112), their interval identical to solar wind arrival from instability between L1 and asymmetrical bow shock terminate a 33-day non-random/cyclically-correlated arrival block of LIGO-Virgo triggers, GPS clock error patent, similar to S190718y, 98% terrestrial BNS trigger and still unretracted.
https://twitter.com/Fulguritics/status/1179907360254390272
https://twitter.com/Fulguritics/status/1180028237658783744:




both events S190930s, S190930t:

event S190930s, 2019-0930 13:36:02 UTC:


event S190930t, 2019-0930 14:34:27 UTC:


event S191105e, 2019-1105 14:35:45 UTC,
LIGO-Virgo arrival time correlations yet again:
https://twitter.com/Fulguritics/status/1192313628902322176
First #O3bisHere trigger #S191105e: 14:35:45 UTC FAR 1/1.3881 yrs FInal O3a trigger #S190930t: 14:34:27 UTC
#S190718y 14:35:32 UTC 98% terrestrial; @mpi_grav
claims display "glitch" prevented prompt notice, timed w/upgraded prob. (87% terrestrial,13% BBH->95% BBH, 5% terrestrial)
https://twitter.com/Fulguritics/status/1192341330174726144




Extreme magnetospheric angle oscillation during first reported O3b trigger, S191105e:



event S191110af, 2019-1110 23:10:58 UTC, UPDATE 19-1115 UTC: RETRACTED https://twitter.com/LIGO/status/1195118903225176064. putative 'burst' transient (unmodeled GW source with amplitude peak at 1781.72 Hz, identical to terrestrial-heliopause LHR (lower hybrid resonance):


event S191117j 2019-1117 06:08:44 UTC RETRACTED:









event S191120aj 2019-1120 16:23:51 UTC RETRACTED:


event S191120at 2019-1120 20:09:03 UTC RETRACTED:

 pair of retracted NSBH ( S191120aj) and MassGap (S191120at) events that occurred bracketing strong periodic correlations 1/||(An-Bn)/(∑ (An,Bn))|| 5-min following event S191120aj and 5-min prior to event #S191120at, with interval ~225 minutes (as 6*37 minute prevailing [well-known recurring mode] magnetopause-ground lag):
pair of retracted NSBH ( S191120aj) and MassGap (S191120at) events that occurred bracketing strong periodic correlations 1/||(An-Bn)/(∑ (An,Bn))|| 5-min following event S191120aj and 5-min prior to event #S191120at, with interval ~225 minutes (as 6*37 minute prevailing [well-known recurring mode] magnetopause-ground lag):

event S191124be 2019-1124 10:00:09 UTC, retracted:






ACE solar wind, event at white line:



 North American ground magnetometers around event:
North American ground magnetometers around event:

event S191212q 2019-1212 08:27:28 UTC RETRACTED:

 ACE IMF:
ACE IMF:



North American ground magnetometers:

event S191213g 2019-12-13 04:34:08 UTC:


event S191213ai 15:59:05 UTC RETRACTED:






event S191215w 1260484270.332015-1215 22:30:52 UTC:





event S191216ap 1260567236.472015-1216 21:33:38 UTC:

















event S191220af 2019-1220 12:24:14 UTC RETRACTED:




event S191222n, 2019-1222, 03:35:37 UTC:






event S191225aq, 1261346253.872019-1225 21:57:15 UTC, RETRACTED:













https://ccmc.gsfc.nasa.gov/cgi-bin/display/RT_t.cgi

https://ccmc.gsfc.nasa.gov/cgi-bin/display/RT_t.cgi
event S200108v 1262512856.562020-0108, 10:00:38 UTC RETRACTED:

First #O3bisHere trigger #S191105e: 14:35:45 UTC FAR 1/1.3881 yrs FInal O3a trigger #S190930t: 14:34:27 UTC
#S190718y 14:35:32 UTC 98% terrestrial; @mpi_grav
claims display "glitch" prevented prompt notice, timed w/upgraded prob. (87% terrestrial,13% BBH->95% BBH, 5% terrestrial)
https://twitter.com/Fulguritics/status/1192341330174726144




Extreme magnetospheric angle oscillation during first reported O3b trigger, S191105e:



event S191110af, 2019-1110 23:10:58 UTC, UPDATE 19-1115 UTC: RETRACTED https://twitter.com/LIGO/status/1195118903225176064. putative 'burst' transient (unmodeled GW source with amplitude peak at 1781.72 Hz, identical to terrestrial-heliopause LHR (lower hybrid resonance):


event S191117j 2019-1117 06:08:44 UTC RETRACTED:









event S191120aj 2019-1120 16:23:51 UTC RETRACTED:


event S191120at 2019-1120 20:09:03 UTC RETRACTED:

 pair of retracted NSBH ( S191120aj) and MassGap (S191120at) events that occurred bracketing strong periodic correlations 1/||(An-Bn)/(∑ (An,Bn))|| 5-min following event S191120aj and 5-min prior to event #S191120at, with interval ~225 minutes (as 6*37 minute prevailing [well-known recurring mode] magnetopause-ground lag):
pair of retracted NSBH ( S191120aj) and MassGap (S191120at) events that occurred bracketing strong periodic correlations 1/||(An-Bn)/(∑ (An,Bn))|| 5-min following event S191120aj and 5-min prior to event #S191120at, with interval ~225 minutes (as 6*37 minute prevailing [well-known recurring mode] magnetopause-ground lag):
- total fractional clock error at 6th #LIGO-Virgo retraction in a row: #MBTAOnline #S191124be (57th trigger by 10:00 UTC!) GPS 0.099619 frozen clock error, same 35±10 Mpc DL as retracted #S190822c (#GstLaL frozen at 0.589203). (MBTAOnline former retraction #S190816i w/FCE 0.757789)


event S191129u, 2019-1129 13:41:06 UTC:


event S191204r, 2019-1204 17:15:51 UTC:


ACE solar wind, event at white line:

Geostationary magnetic field showed sawtooth behavior with quasi-steady ramping and ringing behavior:

Tromso magnetometer around event S191204r (at 17:15:51 UTC); notice behavior of station 8737, which has data loss directly after timing of LIGO-Virgo trigger as global field shows successive substorm formation, possible a sawtooth event:



event S191205ah 2019-1205 21:52:44 UTC:




North American/Pacific USGS magnetometer around event S191204r (at 17:15:51 UTC), with missing data preceding strong sawtooth-ramping quasiperiodic oscillation:



extraordinary coherence in ACE solar wind/IMF parameters (event S191205ah, 21:52:44 UTC, at white bar):

 North American ground magnetometers around event:
North American ground magnetometers around event:
event S191212q 2019-1212 08:27:28 UTC RETRACTED:

 ACE IMF:
ACE IMF:

Tromso Northern ground magnetometers:

North American ground magnetometers:

event S191213g 2019-12-13 04:34:08 UTC:


event S191213ai 15:59:05 UTC RETRACTED:






event S191215w 1260484270.332015-1215 22:30:52 UTC:





event S191216ap 1260567236.472015-1216 21:33:38 UTC:


#LIGO-Virgo #S191216ap, 21:34:01 UTC: "Up until 21:33:21 UTC IceCube was collecting good quality data, at which point power issues at the experimental site caused issues with data quality." https://gcn.gsfc.nasa.gov/other/GW191216ap.gcn3…
NA https://photos.app.goo.gl/oELApi2bhSkwMBrcA…
#LIGO-Virgo event #S191216ap, substorm relax., solar wind-magnetosphere decoupling, global CG lightning burst sync https://photos.app.goo.gl/nxQWqDtCpUDkAyuc7… Earth-facing coronal hole, Microseism (T-storm, wind, earthquake activity)->Livingston down. Evolution of global CG lightning maps all.
#S191216ap sky localization latitude, as usual for #LIGO events, superimposes over centroids on Earth; mis-scaling-related longitude offset of 1.162 from terrestrial source allows radial transformation into BAYESTAR probability domain map. See projections, calculations:
Updated sky map shows 50% confident range restricted to an area 40-42° (previously ~46°), which I calculated to propagate the normal front range for coherent burst from radar-active T-storm domain extrema. Circle degeneracies from critical ellipse mis-scaling preserve measures.
#LIGO-Virgo event #S191216ap, substorm relax., solar wind-magnetosphere decoupling, global CG lightning burst sync https://photos.app.goo.gl/nxQWqDtCpUDkAyuc7… Earth-facing coronal hole, Microseism (T-storm, wind, earthquake activity)->Livingston down. Evolution of global CG lightning maps all.
#S191216ap sky localization latitude, as usual for #LIGO events, superimposes over centroids on Earth; mis-scaling-related longitude offset of 1.162 from terrestrial source allows radial transformation into BAYESTAR probability domain map. See projections, calculations:
Updated sky map shows 50% confident range restricted to an area 40-42° (previously ~46°), which I calculated to propagate the normal front range for coherent burst from radar-active T-storm domain extrema. Circle degeneracies from critical ellipse mis-scaling preserve measures.
Subtended angle delimiting active region is 33.3°, min. at 30°. Reference source and period, #LIGO-Virgo trigger #S191216ap (2019-12-16, 21:34:01 UTC): North American CG during trigger https://photos.app.goo.gl/1zFCAerm3kmMuo9R7… Global CG during trigger https://photos.app.goo.gl/Ps4AoaNmN6TK7d3c6…















event S191220af 2019-1220 12:24:14 UTC RETRACTED:




event S191222n, 2019-1222, 03:35:37 UTC:






event S191225aq, 1261346253.872019-1225 21:57:15 UTC, RETRACTED:










events S200106au 1262370887.292020-0106 18:34:29 UTC and S200106av 2020-0106 18:34:23 UTC, BOTH RETRACTED:



https://ccmc.gsfc.nasa.gov/cgi-bin/display/RT_t.cgi

https://ccmc.gsfc.nasa.gov/cgi-bin/display/RT_t.cgi
event S200108v 1262512856.562020-0108, 10:00:38 UTC RETRACTED:









event S200112r, 2020-0112, 15:58:38 UTC:







S200112r (15:58:38 UTC) arrived within substorm trigger interval of S200105ae (16:24:26 UTC, 97% terrestrial source prob, FAR 24.21 per year, much higher than O2 relaxed limit of ~1 per 33 days). S200105ae arrived within one minute of UTC ToD of retracted NSBH trigger S191120aj, which preceded retracted MassGap trigger S191120at on same day.
event S200114f 1263002916.24Jan. 14, 2020 02:08:18 UTC:
#S200114f #LIGO-Virgo trigger; no class, source prob, or DL, but narrow sky loc.
O2 GW170608/GW170818 ToA in same 25-min. window, like other proximal triggers.
#S200114f 02:08:18 UTC, Burst transient, CWB search, at central freq. 64.69 [Hz] lasting 0.01 sec. gcn.gsfc.nasa.gov/notices_l/S200
burst transient, 02:08:46 UTC; coherent shock sequence at L1 00:52-1:38 UTC, invariant solar wind v:lag ensemble converge at LVC event, w/central freq., 64.69 Hz as central val. for 10th Schumann res. mode ~64.62 Hz|0.88 c arxiv.org/pdf/1707.09047
(quasiperiodic correlation|sawtooth/shear/injection/ saddle modes)
burst is already propaganda. Many LVC events have false alarm rates of >1/year: "As Andy said...gravitational wave detectors do sometimes detect false positives, about once every 25 years. So that is something to keep in mind." earthsky.org/space/ligo-gra











https://ccmc.gsfc.nasa.gov/cgi-bin/display/RT_t.cgi



event S200116ah 1263211020.172020-0116, 11:56:42 UTC RETRACTED:





event S200116ah 1263211020.172020-0116, 11:56:42 UTC RETRACTED:


https://ccmc.gsfc.nasa.gov/cgi-bin/display/RT_t.cgi
#S200116ah #S200115j #S200114f #S200112r




event S200128d 2020-0128, 02:20:11 UTC:




#S200116ah #S200115j #S200114f #S200112r
ACE interplanetary magnetic field MAG and solar wind SWEPAM during seven days, three days, and 24-hrs -
events indicated by white bars:




event S200128d 2020-0128, 02:20:11 UTC:





https://ccmc.gsfc.nasa.gov/cgi-bin/display/RT_t.cgi



event S200129m 2020-0129, 06:54:58 UTC:


BATSRUS magnetosphere to 15 RE/IMF connectivity-mean magnetospheric field line models surrounding event S200129m:







ACE SWEPAM/MAG solar wind and interplanetary magnetic field indices and functions with calculated lags, empirical constants:









BATSRUS magnetosphere to 15 RE/IMF connectivity-mean magnetospheric field line models surrounding event S200129m:







ACE SWEPAM/MAG solar wind and interplanetary magnetic field indices and functions with calculated lags, empirical constants:




https://ccmc.gsfc.nasa.gov/cgi-bin/display/RT_t.cgi





















event S200219ac, 2020-0219 09:44:15 UTC:







further development of correlated magnetospheric state:




event S200224ca, 2020-0224 22:22:34 UTC:













event S200225q, 2020-0225 06:04:21 UTC:






event S200302c, 2020-0302 1267149509.5201:58:11 UTC:









 https://twitter.com/Fulguritics/status/1234619528669065216https://twitter.com/Fulguritics/status/1234619532137811968
https://twitter.com/Fulguritics/status/1234619528669065216https://twitter.com/Fulguritics/status/1234619532137811968
event S200303ba, 2020-0303 12:15:48 UTC RETRACTED:









event S200208q, 2020-0208 13:01:17 UTC:


















event S200219ac, 2020-0219 09:44:15 UTC:







further development of correlated magnetospheric state:

















event S200225q, 2020-0225 06:04:21 UTC:















 https://twitter.com/Fulguritics/status/1234619528669065216https://twitter.com/Fulguritics/status/1234619532137811968
https://twitter.com/Fulguritics/status/1234619528669065216https://twitter.com/Fulguritics/status/1234619532137811968event S200303ba, 2020-0303 12:15:48 UTC RETRACTED:








RETRACTED #LIGO-Virgo #S200303ba 12:15:48 UTC BBH 86% FAR 1/2.4086 yrs NO CLOCK ERROR! burst-synced global CG #lightning photos.app.goo.gl/pv7UVxPVtrvBys #spaceweather [cf. unretracted #S200302c BBH 89% FAR 1/3.3894 yrs, clock error, mirror point correlation w/S200303ba, sawtooth event]

event S200308e, 2020-0308 01:19:27 UTC retracted:






event S200311bg, 2020-0311 11:58:53 UTC:








#S200311bg 11:58:53 UTC - coronal flare/flow/CME solutions for this (and correlation to prior March events: #S200302c, #S200303ba (retracted), and #S200308e (retracted):
event S200316bj, 2020-0316 21:57:56 UTC:









Further information on research involving lightning driving by magnetospheric coupling during interplanetary magnetic field (IMF) parametric coherence:
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs11214-011-9859-8
https://www.hindawi.com/journals/ijge/2011/971302/
https://books.google.com/books?id=rrSgz8l0EI0C&pg=PA101&lpg=PA101&dq=magnetosphere+coupling+OR+driving+lightning&source=bl&ots=V0Xjrb5tIp&sig=cZP9ZXltDbiFk1tywU20t6v6UoY&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwiC5pyRosvbAhWBr4MKHfksCwAQ6AEIWzAI#v=onepage&q=magnetosphere%20coupling%20OR%20driving%20lightning&f=false
https://books.google.com/books?id=bCEiDQAAQBAJ&pg=PA128&lpg=PA128&dq=magnetosphere+coupling+OR+driving+lightning&source=bl&ots=jIRyfRkwH4&sig=4FEjamvpVhb0vMRF4Ag8o03CtRE&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwiC5pyRosvbAhWBr4MKHfksCwAQ6AEISTAE#v=onepage&q=magnetosphere%20coupling%20OR%20driving%20lightning&f=false

event S200316bj, 2020-0316 21:57:56 UTC:









SOLAR WIND PROTONS AND RAREFACTION DURING GW EVENTS: TUNNELING MAGNETOSPHERIC PARTICLE OUTFLOW FEEDBACK DRIVEN DIPOLARIZATION IN TRANS-CONFORMAL/SCALE-INVARIANT nth-ORDER GENERATION OF INTERPLANETARY VACUUM DELTA SHOCKS
A discharge pulse count trend for five-minute 𝜏(5[3,2]) impulse triggers (global-coherent [non-random] two-phase duty cycle) terminating through bursts of near-simultaneous cloud-ground discharge follows CG quiet periods with broadband radio interference, enhanced (often band-narrowed/high-Q Schumann resonance leakage), and IC/GC phase of approx. 2-3 minutes prior, conforming to the mean length equal to stated and well-recognized correlated cycle lengths from prior analyses (see On the time lags of the LIGO signals); high SNR strain data are seemingly phase and amplitude locked between detectors during these periods. It is not well-known or considered during hypothesis development and testing that [ground strike] lightning can [near] simultaneously respond with stable phase coupling to geomagnetic, ionospheric, and magnetospheric coherence and dipolarization fronts/shocks/reconnection during these unusual global discharge correlations, bound to near-exact 2, 3, and 5-minute increments. Geographic correlations between active regions on Earth also occur during these correlated impulse-locked phases, especially between Central-Eastern North America and Southern Australia.

COMPLEX PHASE SHOCK COUPLING BETWEEN SOLAR WIND, MAGNETOSPHERE, AND TERRESTRIAL GROUND: RECONNECTION AND SAWTOOTH OSCILLATIONS
Solar wind phase and amplitude locking between noise correlation phases during GW150914 and GW151012 (LVT151012) show exact data gaps as well, which is not an artifact of data processing. Gaps in ACE or GOES satellite data indicate excessive charging has occurred or the fidelity of the data have been rejected during post-processing before distribution. The pulse periodicity in the global lightning activity around GW trigger times is represented as vertical bars, to familiarize the reader with the extended significance of such unusual lightning impulse/trigger behavior:

1. [prelim.] G13 magnetometer data with coincident lightning activity from Oklahoma storm active during GW150914 (grey bar); (light blue) the PACF of the PSD (DCT-II of the PACF) of 35-350 Hz bandpassed-unwhitened 16384 Hz time domain strain data from Livingston for the 0.2 s event, showing uncanny scaled conformity to the sawtooth event and to the impulsive triggering of globally-coherent lightning; [green] the PACF of the Hanford 35-350 Hz bandpassed-unwhitened 16384 Hz time series for the 0.2 s GW150914 event.
2. [prelim] lightning discharge model around GW150914 (black is back-shifted five minutes) and red with four parameters from GOES13 512 ms proton flux (magnetometer), clearly showing a magnetospheric sawtooth event was underway, correlated with the duration of inter-detector cross-correlations as noted by several authors:

1. [prelim.] G13 magnetometer data with coincident lightning activity from Oklahoma storm active during GW150914 (grey bar); (light blue) the PACF of the PSD (DCT-II of the PACF) of 35-350 Hz bandpassed-unwhitened 16384 Hz time domain strain data from Livingston for the 0.2 s event, showing uncanny scaled conformity to the sawtooth event and to the impulsive triggering of globally-coherent lightning; [green] the PACF of the Hanford 35-350 Hz bandpassed-unwhitened 16384 Hz time series for the 0.2 s GW150914 event.
2. [prelim] lightning discharge model around GW150914 (black is back-shifted five minutes) and red with four parameters from GOES13 512 ms proton flux (magnetometer), clearly showing a magnetospheric sawtooth event was underway, correlated with the duration of inter-detector cross-correlations as noted by several authors:
Magnetosphere B[[z|y],[z|x],[x|y]] scatterplots on N=7 GW days for available data (data colored according to scheme in legend of first graph):






Further established research involving magnetospheric sawtooth events, optimal substorm crossover phases displaying interplanetary magnetic field (IMF) parametric coherence:
Further information on research involving lightning driving by magnetospheric coupling during interplanetary magnetic field (IMF) parametric coherence:
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs11214-011-9859-8
https://www.hindawi.com/journals/ijge/2011/971302/
https://books.google.com/books?id=rrSgz8l0EI0C&pg=PA101&lpg=PA101&dq=magnetosphere+coupling+OR+driving+lightning&source=bl&ots=V0Xjrb5tIp&sig=cZP9ZXltDbiFk1tywU20t6v6UoY&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwiC5pyRosvbAhWBr4MKHfksCwAQ6AEIWzAI#v=onepage&q=magnetosphere%20coupling%20OR%20driving%20lightning&f=false
https://books.google.com/books?id=bCEiDQAAQBAJ&pg=PA128&lpg=PA128&dq=magnetosphere+coupling+OR+driving+lightning&source=bl&ots=jIRyfRkwH4&sig=4FEjamvpVhb0vMRF4Ag8o03CtRE&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwiC5pyRosvbAhWBr4MKHfksCwAQ6AEISTAE#v=onepage&q=magnetosphere%20coupling%20OR%20driving%20lightning&f=false














No comments:
Post a Comment